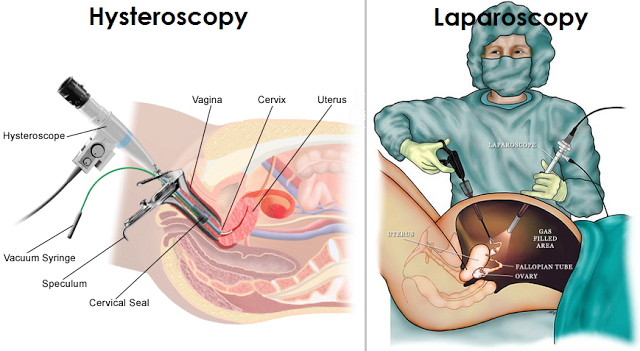
Hysteroscopy
A hysteroscopy is a procedure used to diagnose and treat specific problems within the uterus. It is done using a specialised thin tube called a hysteroscope. The hysteroscope is inserted into the vagina and a small viewing devise is used to examine inside the uterus and cervix.
A diagnostic hysteroscopy can be used to identify problems in the uterus, such as septums. It can also be performed to corroborate findings of other tests, such as x-rays. The procedure is often done at the same time as a laparoscopy.
An operative hysteroscopy may be used to treat a range of uterine conditions. This may include the removal of fibroids, adhesions and polyps that can lead to infertility. Women who suffer from abnormal bleeding may undergo a hysteroscopy as part of an endometrial ablation procedure.
www.amitamin.com/en/fertilsan-m New life deserves the best possible start!We provide the essential building blocks for this.
Prior to a hysteroscopy, the doctor may prescribe a sedative to relax the body. In some instances, anesthesia isn’t necessary. This is usually the case in diagnostic hysteroscopy using a microhysteroscope (tube less than 5 mm wide).
When anesthesia is needed, it may be local, regional or general. This depends on whether other procedures are going to be performed simultaneously and the facility where the hysteroscopy is being conducted. Generally, the stages of a hysteroscopy are as follows:
- The cervix will be dilated using a device called a speculum.
- The hysteroscope is inserted through the vagina and cervix, and then into the uterus.
- A liquid solution or carbon dioxide gas is used to expand the uterus and remove any mucus and blood.
- The uterus and fallopian tubes openings are examined with a light shone through the hysteroscope.
- If surgery is needed, small instruments will be introduced into the uterus via the hysteroscope. In some cases a biopsy test may be performed if there are signs of an endometrial condition.
Duration
A hysteroscopy is a minor surgical procedure that take anywhere from 5 minutes to more than an hour. The duration depends on if the procedure is diagnostic or operative. Rarely will a patient need to stay in hospital overnight. If an overnight stay is required, it’s usually to monitor the patients reactions to the anesthesia.
Success Rate
Hysteroscopy is generally a very well tolerated and effective treatment for women with intrauterine pathologies. However, there is no general consensus on its effectiveness for improving fertility. The procedure is generally not recommended as the first course of action to treat infertility.
Nevertheless, in instances where assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs) have failed, a hysteroscopy can be effective for improving reproductive outcomes. Researchers are calling for more studies into the benefits of hysteroscopy procedures to improve pregnancy rates in subfertile women[1]“Bosteels, J. et.al. (2009). The effectiveness of hysteroscopy in improving pregnancy rates in subfertile women without other gynaecological symptoms: A systematic review. Human Reproduction … Continue reading.
Cost
In the UK, hysteroscopy costs are generally covered by most medical insurance policies. However, it’s important to check with your insurer. In the case where you are paying for your own treatment, ensure that you ask for a written quote beforehand. This should include the surgeon’s fee, hospital/clinic charges, and the anesthetist’s fee.
The cost varies depending on where the procedure is being performed and whether it is part of another procedure, such as a laparoscopy for example. Generally costs for a diagnostic hysteroscopy are much lower than for an operative hysteroscopy.
In a private clinic the cost of a hysteroscopy can vary from £775 – £6, 903[2]”https://www.privatehealth.co.uk/hospitaltreatment/whatdoesitcost/hysteroscopy/”. The average cost is £2, 380. This may not include initial consultation costs.
In some cases the NHS may cover hysteroscopy surgery. This is usually only once all other avenues have been explored to diagnose an ongoing health problem, such as endometriosis for example. Patients will require a referral from a GP to see a gynaecologist or specialist health clinic.
Side Effects
Some of the side effects include hot flashes, cramping, bloating, vaginal dryness and headaches. These reactions should only occur for a couple of days. It’s important to contact your doctor if you experience severe abdominal pain, fever, or heavy vaginal discharge or bleeding.
Candidates for hysteroscopy
If you are having trouble falling pregnant, a fertility specialist may recommend having a hysteroscopy to determine if there are any problems with your uterus. However, in most cases other avenues will explored before performing a hysteroscopy.
This procedure may also be recommended for women experiencing heavy bleeding, bleeding between menstruations and after sexual intercourse or menopause, pelvic pain, repeated miscarriage, or unusual virginal discharge.
A hysteroscopy cannot be performed during pregnancy, or if you suffer from cervical cancer, genital inflammation, or other serious health problems. In these cases, alternative treatments may be available.

Dr. Kooner is Deputy Director of The Advanced Fertility Center of Chicago and has been a Specialist in Fertility Treatment since 1999.
As well as the areas that the clinic specialises in general, he is particularly interested in managing oocyte donation, female same-sex couples, single women having sperm donation and those considering egg freezing.
Dr. Kooner regularly speaks at fertility meetings. He has published in national journals and constantly contributes to the fertility research and publications from Advanced Fertility Center of Chicago.
References
| ↑1 | “Bosteels, J. et.al. (2009). The effectiveness of hysteroscopy in improving pregnancy rates in subfertile women without other gynaecological symptoms: A systematic review. Human Reproduction Update, Volume 16, Issue, 1, (pp. 1-11).” |
|---|---|
| ↑2 | ”https://www.privatehealth.co.uk/hospitaltreatment/whatdoesitcost/hysteroscopy/” |



